Categories
Problems that solves
Aging IT infrastructure
High costs of IT personnel
Lengthy production timelines
Values
Reduce Costs
Reduce Production Timelines
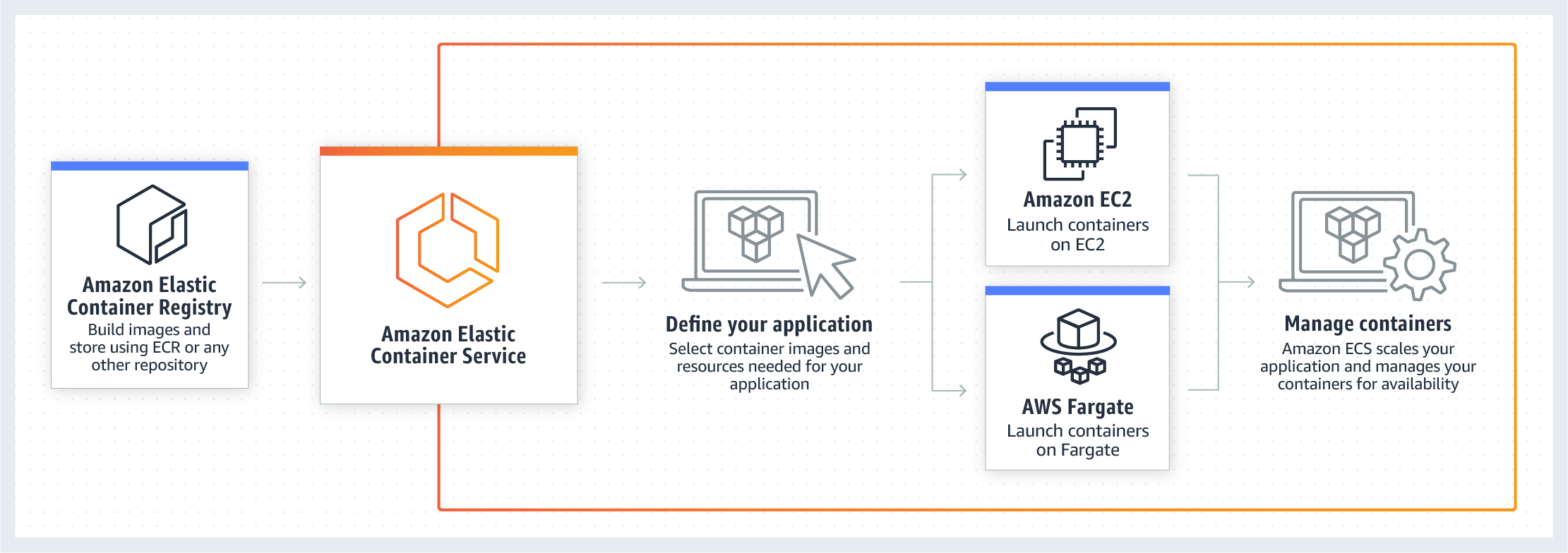
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
Amazon Elastic Container Service - run containerized applications in production.
About Product
Description
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a highly scalable, high-performance container orchestration service that supports Docker containers and allows you to easily run and scale containerized applications on AWS. Amazon ECS eliminates the need for you to install and operate your own container orchestration software, manage and scale a cluster of virtual machines, or schedule containers on those virtual machines.
With simple API calls, you can launch and stop Docker-enabled applications, query the complete state of your application, and access many familiar features such as IAM roles, security groups, load balancers, Amazon CloudWatch Events, AWS CloudFormation templates, and AWS CloudTrail logs.
FEATURES:
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) allows you to easily run, scale, and secure Docker container applications on AWS. Applications packaged as containers locally will deploy and run in the same way as containers managed by Amazon ECS. Amazon ECS eliminates the need to install, operate, and scale your own container orchestration and cluster management infrastructure, and allows you to focus on the resource needs and availability requirements of your containerized application.
Amazon ECS enables you to grow from a single container to thousands of containers across hundreds of instances without creating additional complexity in how you run your application. You can run anything: applications, batch jobs, or microservices. Amazon ECS abstracts away all the complexity of the infrastructure so you can focus on designing, building, and running containerized applications.
With Amazon ECS, you can use AWS Fargate to fully manage your infrastructure and just focus on deploying containers Or, you can choose to have complete visibility and control of your underlying server cluster from creating and terminating Docker containers to viewing detailed cluster state information. You can integrate and use your own container scheduler or connect Amazon ECS into your existing software delivery process, such as continuous integration and delivery systems.
AWS Fargate Support
AWS Fargate technology is available with Amazon ECS. With AWS Fargate, you no longer have to select Amazon EC2 instance types, provision and scale clusters, or patch and update each server. You do not have to worry about task placement strategies, such as binpacking or host spread and tasks are automatically balanced across availability zones. Fargate manages the availability of containers for you. You just define your application’s requirements, select Fargate as your launch type in the console or CLI, and Fargate takes care of all the scaling and infrastructure management required to run your containers.
For developers who require more granular, server-level control over the infrastructure, Amazon ECS EC2 launch type allows you to manage a cluster of servers and schedule placement of containers on the servers.
Development
Docker Support
Amazon ECS supports Docker and enables you to run and manage Docker containers. Applications you package as a container locally will deploy and run on Amazon ECS without the need for any configuration changes.
Windows Containers Compatibility
Amazon ECS supports management of Windows containers. An Amazon ECS-optimized Windows Amazon Machine Image (AMI) provides enhanced instance and container launch time performance and visibility into CPU, memory utilization, and reservation metrics.
Local Development
The Amazon ECS CLI allows you to simplify your local development experience as well as easily set up and run your containers on Amazon ECS. The Amazon ECS CLI supports Docker Compose, an open-source tool for defining and running multi-container applications. You can apply the same Compose definition used to define a multi-container application on your development machine as well as in production. The Amazon ECS CLI is open-source.
Repository Support
Amazon ECS can be used with any third-party hosted Docker image repository or accessible private Docker registry, such as Docker Hub and Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR). All you need to do is specify the repository in your task definition and Amazon ECS retrieves the appropriate images for your applications.
Management
Task Definitions
Amazon ECS allows you to define tasks through a declarative JSON template called a Task Definition. Within a Task Definition you can specify one or more containers that are required for your task, including the Docker repository and image, memory and CPU requirements, shared data volumes, and how the containers are linked to each other. You can launch as many tasks as you want from a single Task Definition file that you can register with the service. Task Definition files also allow you to have version control over your application specification.
Programmatic Control
Amazon ECS provides you with a set of simple API actions to allow you to integrate and extend the service. The API actions allow you to create and delete clusters, register and deregister tasks, launch and terminate Docker containers, and provide detailed information about the state of your cluster and its instances. You can also use AWS CloudFormation to provision Amazon ECS clusters, register task definitions, and schedule containers.
Container Deployments
Amazon ECS allows you to easily update your containers to new versions. You can upload a new version of your application task definition, and the Amazon ECS scheduler automatically starts new containers using the updated image and stop containers running the previous version. Amazon ECS automatically registers and deregisters your containers from the associated Application Load Balancer.
Blue/Green Deployments
Blue/green deployments with AWS CodeDeploy help you minimize downtime during application updates. You can launch a new version of your Amazon ECS service alongside the old version and test the new version before you reroute traffic. You can also monitor the deployment process and rapidly rollback if there is an issue.
Container Auto-Recovery
The Amazon ECS will automatically recover unhealthy containers to ensure that you have the desired number of containers supporting your application.
Scheduling
Amazon ECS includes multiple scheduling strategies that place containers across your clusters based on your resource needs (for example, CPU or RAM) and availability requirements. Using the available scheduling strategies, you can schedule batch jobs, long-running applications and services, and daemon processes.
Task Scheduling. Amazon ECS task scheduling allows you to run processes that perform work and then stop, such as batch processing jobs. Task scheduling can start tasks manually, automatically from a queue of jobs, or based on a time interval that you define.
Service Scheduling. Amazon ECS service scheduling allows you to run stateless services and applications. This scheduling strategy ensures that a specified number of tasks are constantly running and restarts tasks if they fail. You can make sure that tasks are registered against an Elastic Load Balancing load balancer and can perform health checks that you define for your running tasks.
Daemon Scheduling. Amazon ECS daemon scheduling automatically runs the same task on each selected instance in your ECS cluster. This makes it easy to run tasks that provide common management functionality for a service like logging, monitoring, or backups.
Task Placement
Amazon ECS allows you to customize how tasks are placed onto a cluster of EC2 instances based on built-in attributes such as instance type, Availability Zone, or custom attributes that you define. You can use attributes such as environment = production to label resources, use the list API actions to find those resources, and use the RunTask and CreateService API actions to schedule tasks on those resources.
With Amazon ECS, you can also use placement strategies such as bin pack and spread to further define where tasks are placed. Policies can be chained together to achieve sophisticated placement capabilities without writing any code.
Task placement policies are not utilized with the AWS Fargate Launch Type.
Networking and Security
Service Discovery
Amazon ECS is integrated with AWS Cloud Map to make it easy for your containerized services to discover and connect with each other. AWS Cloud Map is a cloud resource discovery service. With Cloud Map, you can define custom names for your application resources, and it maintains the updated location of these dynamically changing resources. This increases your application availability because your web service always discovers the most up-to-date locations of its resources.
Service Mesh
Service mesh makes it easy to build and run complex microservices applications by standardizing how every microservice in the application communicates. AWS App Mesh is a service that makes it easy to configure part of your application for end-to-end visibility and high-availability. To use App Mesh, add the Envoy proxy image to the ECS task definition. App Mesh manages Envoy configuration to provide service mesh capabilities. App Mesh exports metrics, logs, and traces to the endpoints specified in the Envoy bootstrap configuration provided. App Mesh provides an API to configure traffic routes, circuit breaking, retries, and other controls between microservices that are mesh-enabled.
Task Networking
Amazon Elastic Container Service supports Docker networking and integrates with Amazon VPC to provide isolation for containers. This gives you control over how containers connect with other services and external traffic. With Amazon ECS, you can choose between four networking modes for your containers that cater towards different use cases:
- Task Networking/awsvpc. This mode assigns each running ECS task a dedicated elastic networking interface, allowing containers full networking features in a VPC, just like EC2 instances.
- Bridge. This mode creates a Linux bridge that connects all containers running on the host in a local virtual network, which can be accessed through the host's default network connection.
- Host. This mode adds containers directly to the host’s network stack, exposing containers on the host's network with no isolation.
- None. This mode disables external networking for containers.
Scheme of work
Competitive products
User features
Roles of Interested Employees
Chief Executive Officer
Chief Information Officer
Organizational Features
Internet access is available for employees